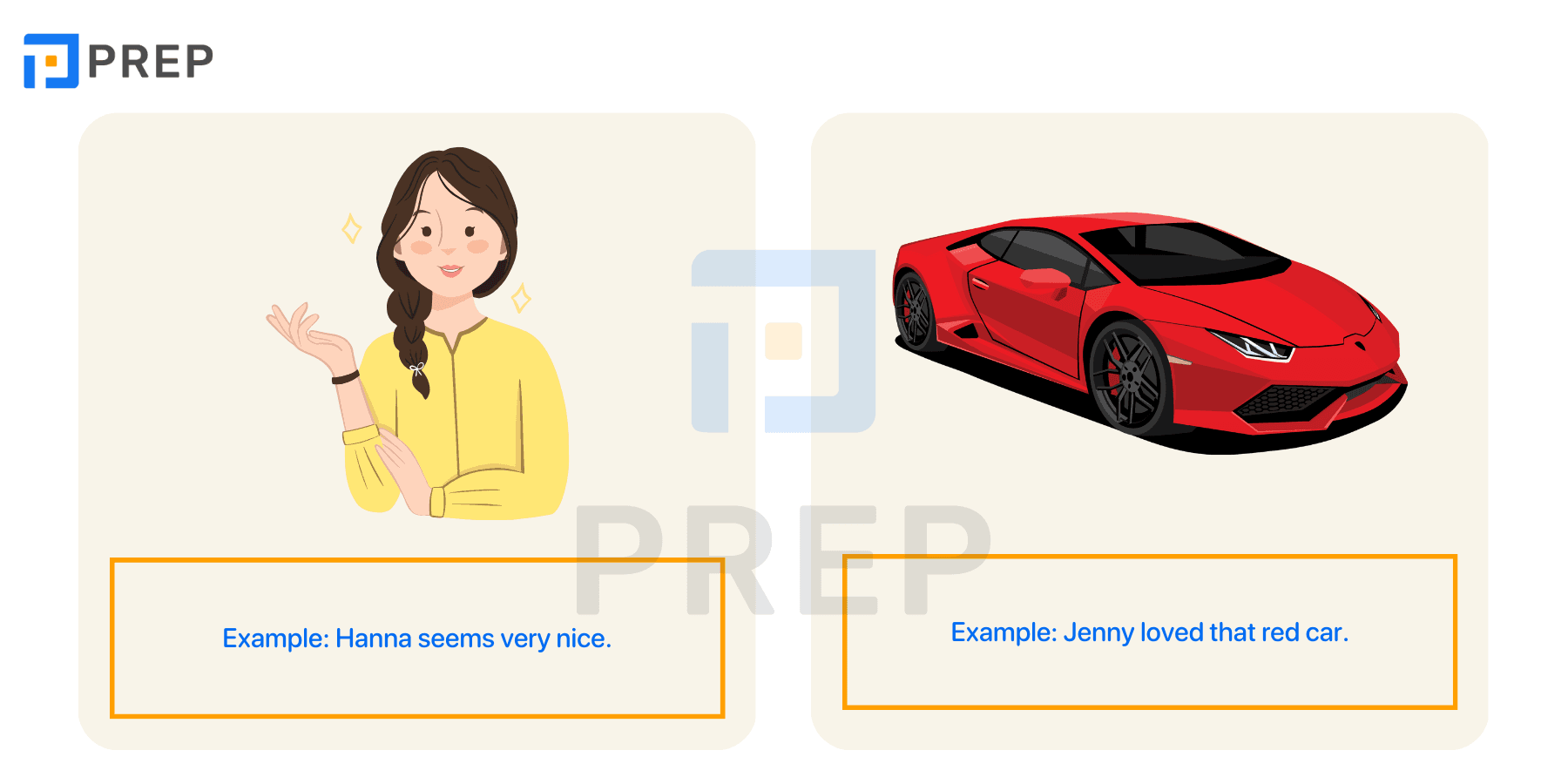
Short Adjectives and Long Adjectives in Comparisons
Understanding the difference between short adjectives and long adjectives is essential for accurate English communication. In this guide, you'll learn how to form comparatives and superlatives, recognize common exceptions, and avoid typical grammar mistakes—all with practical examples and exercises.

I. What Are Short and Long Adjectives?
Short adjectives and long adjectives are classified based on the number of syllables they have. This distinction is important in English grammar, especially when forming comparative and superlative forms.
- Short adjectives usually have one syllable, or sometimes two syllables that end in -y, -er, or -ow. They are typically used with the “-er” and “-est” endings when making comparisons.
- Long adjectives have two or more syllables (especially those that don't end in -y), and they require “more” or “most” to form comparisons.
Key Differences Between Short and Long Adjectives
|
Feature |
Short Adjectives |
Long Adjectives |
|
Syllables |
Mostly 1 syllable, some 2 |
2 or more syllables |
|
Comparative form |
adjective + -er |
more + adjective |
|
Superlative form |
the + adjective + -est |
the most + adjective |
|
Examples (Comparative) |
taller, faster |
more difficult, more expensive |
|
Examples (Superlative) |
the tallest, the fastest |
the most difficult, the most useful |
Understanding the difference between short and long adjectives helps you:
- Use correct grammar when comparing items.
- Avoid common mistakes like “more faster” or “beautifuller.”
- Improve accuracy in writing essays, speaking in exams (like IELTS, TOEIC), and daily English communication.
II. Rules for Using Short and Long Adjectives in Comparisons
In English grammar, short and long adjectives follow different rules when used to make comparisons. Understanding these rules helps English learners avoid common mistakes and construct grammatically correct sentences.
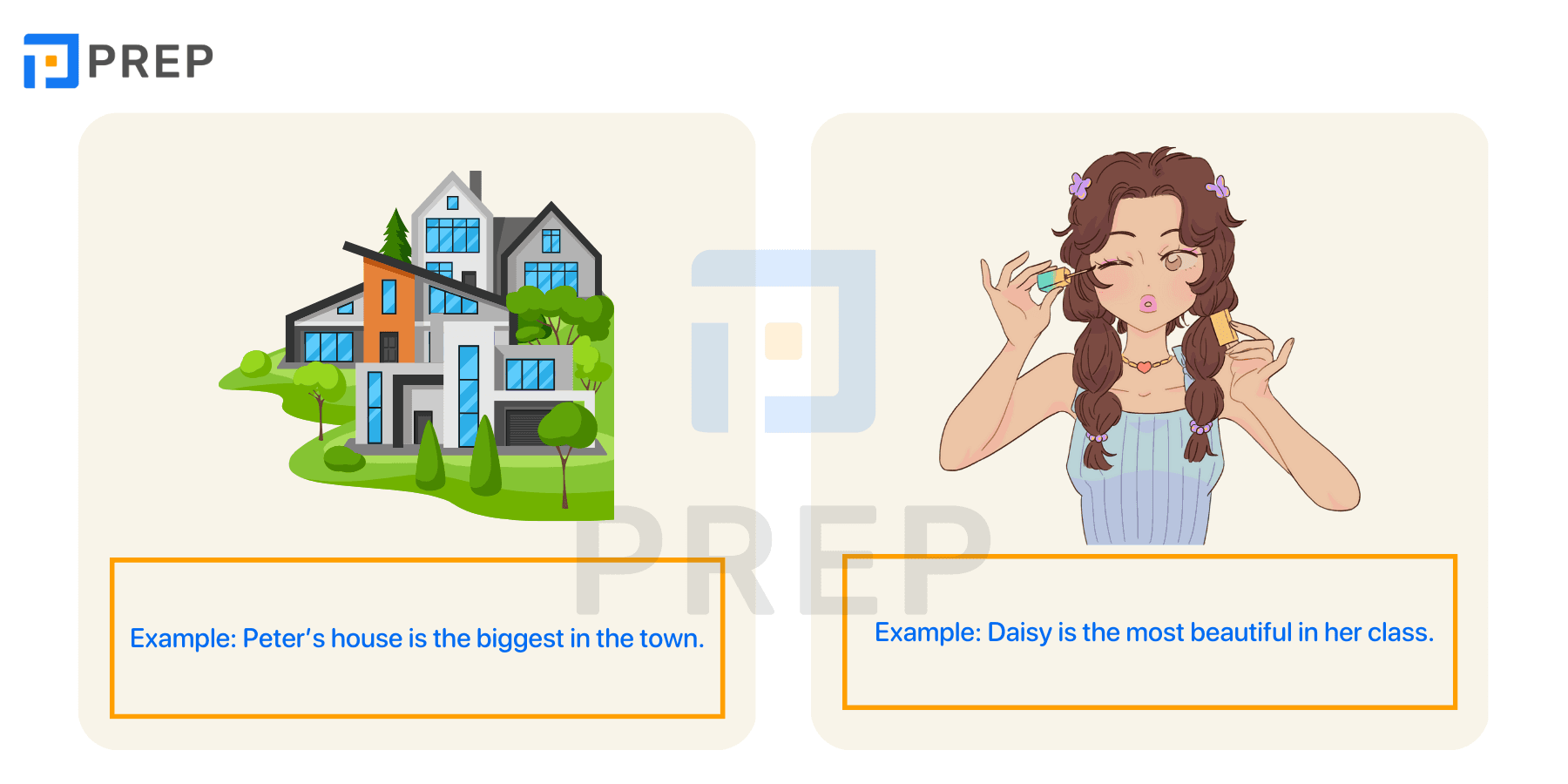
1. Comparative and Superlative Forms
In English, we use comparative forms to compare two people, objects, or ideas, and superlative forms to compare more than two or identify something as the most or least in a group. How you form these depends on whether the adjective is short or long.
Rules for Short Adjectives
Short adjectives typically have one syllable, or two syllables ending in “-y”, “-le”, or “-ow.” They generally form comparatives and superlatives by adding suffixes.
- Comparative: Add -er to the adjective
- Superlative: Add -est to the adjective, and put “the” in front
Examples:
|
Base Adjective |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
tall |
taller |
the tallest |
|
big |
bigger |
the biggest |
|
happy |
happier |
the happiest |
|
simple |
simpler |
the simplest |
Spelling rules to remember:
- If the adjective ends in -e, just add -r or -st: nice → nicer → the nicest
- If the adjective ends in a consonant preceded by a single vowel, double the consonant: hot → hotter → the hottest
- If it ends in “-y”, change “-y” to “-i” before adding -er or -est: happy → happier → the happiest
Rules for Long Adjectives
Long adjectives (two or more syllables, not ending in -y or -le) form their comparisons using “more” for comparative and “most” for superlative. You do not add any suffix to these adjectives.
- Comparative: more + adjective
- Superlative: the most + adjective
Examples:
|
Base Adjective |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
expensive |
more expensive |
the most expensive |
|
comfortable |
more comfortable |
the most comfortable |
|
interesting |
more interesting |
the most interesting |
Using the wrong form, like “expensiver” or “comfortablest”, is grammatically incorrect.
When to Use Comparative vs. Superlative
- Comparative: Use when comparing two things - This book is more interesting than that one; My house is bigger than yours.
- Superlative: Use when comparing three or more things - This is the most comfortable chair in the room; He is the tallest player on the team.
2. Common Exceptions and Irregular Adjectives
Although most adjectives follow predictable rules when forming the comparative and superlative, English has a number of irregular adjectives that do not use –er, –est, more, or most in the usual way. These exceptions are important to learn because they are frequently used in both spoken and written English.
Irregular Adjective Forms
Some adjectives change completely in their comparative and superlative forms. You simply need to memorize these:
|
Base Adjective |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
good |
better |
the best |
|
bad |
worse |
the worst |
|
far |
farther / further |
the farthest / the furthest |
|
little (amount) |
less |
the least |
|
much / many |
more |
the most |
Usage examples:
- This laptop is better than my old one.
- She's the best dancer in the class.
- We had less time than expected.
- He earns the most money in the department.
Note: Farther and further are often used interchangeably, though farther typically refers to physical distance and further to figurative or abstract distance.
Two-Syllable Adjectives with Flexible Forms
Some two-syllable adjectives can take either the "-er/-est" ending or be used with “more/most”. Both forms are often considered correct, depending on the style (informal vs. formal) and regional preference.
Examples:
|
Adjective |
Option 1 |
Option 2 |
|
clever |
cleverer → the cleverest |
more clever → the most clever |
|
quiet |
quieter → the quietest |
more quiet → the most quiet |
|
narrow |
narrower → the narrowest |
more narrow → the most narrow |
In general:
- The -er/-est form is more common and sounds more natural in everyday English.
- The more/most form can sound a bit more formal or appear in academic texts.
A frequent error is incorrectly combining both comparative constructions in one adjective (called double comparatives), such as: "more faster", "most easiest", "more better"
These are incorrect. You must choose either the suffix (-er/-est) or use the word more/most, not both. Correct forms:
- faster (not more faster)
- the easiest (not most easiest)
- better (not more better)
By learning these exceptions and being careful with flexible adjectives, you’ll avoid common grammar mistakes and sound more fluent and accurate in English.
III. Common Mistakes Learners Make with Adjectives
English learners often make small but meaningful mistakes when using adjectives in comparisons — either by mixing rules, misapplying patterns, or relying on literal translations from their native language. Understanding these common errors can help you avoid losing marks in exams and speak more naturally in real-life conversations.
|
Mistake Type |
Incorrect Example |
Correct Version |
|
Using both “more” and “-er” together |
more faster, more cheaper |
faster, cheaper |
|
Using “-er” or “-est” with long adjectives |
beautifuller, comfortablest |
more beautiful, the most comfortable |
|
Overusing “very” with basic adjectives |
very good, very tired |
excellent, exhausted |
|
Applying regular rules to irregular adjectives |
more better, badder, more less |
better, worse, less |
|
Forgetting “the” in superlative forms |
She is tallest in the class. |
She is the tallest in the class. |
|
Comparison with wrong adjective type |
the most short, more cold |
the shortest, colder |
|
Treating two-syllable flexible adjectives as long |
more clever, more narrow |
cleverer, narrower (also acceptable: more clever) |
IV. Exercises on Short adjectives and Long Adjectives with Answers
The best way to master short and long adjectives is through practice. Below are a few easy exercises covering their basic usage, comparative and superlative forms, and common error correction.
Exercise 1: Below is the Short and Long Adjectives list. Please differentiate them and fill in the corresponding column.
small, thin, difficult, cheap, expensive, wonderful, thick, enjoyable, ambitious, fast, ugly, terrible.
Exercise 2: Choose the correct answer
-
Jenny’s house is _______ than mine.
A. smaller
B. the smallest
C. the smaller
-
Harry bought _______ T-shirt from this shop.
A. the cheaper
B. the cheapest
C. cheaper
-
Kathy is _______ than her mother.
A. older
B. the older
C. the oldest
Answer key
Exercise 1:
|
Short adjectives |
Long adjectives |
|
small, thick, thin, cheap, fast, ugly. |
difficult, wonderful, ambitious, terrible, expensive, enjoyable. |
Exercise 2:
-
A
-
B
-
A
V. Master IELTS Like a Pro
This article has provided the complete knowledge about short adjectives and long adjectives in English that PREP has compiled for you. Hopefully, you have a clear understanding of short and long adjectives in English. Please refer to the appropriate learning paths at PREP to achieve your desired goals by check out our advanced IELTS online prep programs.

Hi I'm Chloe, and I am currently serving as an Product Content Administrator at Prep Education. With over five years of experience in independent online IELTS study and exam preparation, I am confident in my ability to support learners in achieving their highest possible scores.
Comment
Premium content
View allPersonalized roadmap
Most read












